An ectopic (extrauterine) pregnancy is when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, in a location that cannot support its growth. If an egg remains in an unusual position, it will not develop into a baby and the mother's health may be at risk if the pregnancy continues.
There are high risks that can lead to a medical emergency, so an ectopic pregnancy must be treated quickly. We tell you everything you need to know in this article.
What does extrauterine (ectopic) pregnancy mean?
A normal pregnancy is one that forms and develops inside the uterus (intrauterine), after fertilization of the egg in the fallopian tube. It then migrates to the uterus, where it will implant within 5-6 days of fertilization and lead to pregnancy. Once this is formed, the entire reproductive apparatus changes its behavior, one of the first signals being the absence of menstruation.
What happens in case of an ectopic pregnancy? The fertilized egg no longer reaches the uterus and is positioned differently, a situation that can have serious consequences. Complications of an ectopic pregnancy can endanger the health and even the life of the mother.
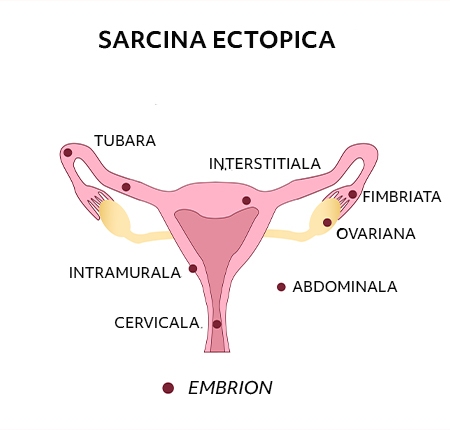
There are several types of ectopic pregnancy, depending on where it forms. Thus, ectopic pregnancy can occur:
at the level of a fallopian tube (tubal pregnancy) - in 90% of cases;
at the level of an ovary;
at the level of the cervix (cervical pregnancy);
in the abdominal cavity.
Ectopic pregnancy - Symptoms & signs
The initial symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy can be very similar to the typical symptoms of a normal pregnancy. We have a separate blog article where we told you all about the first signs of pregnancy . You may not even notice any symptoms at first, and if you take a pregnancy test it will come back positive. However, an ectopic pregnancy cannot continue normally. 
If you have symptoms, they tend to develop between the 4th and 12th week of pregnancy. These may include a combination of:
pain in the pelvic area - often, the pain can be concentrated on only one part of the pelvis, the one where the pregnancy was formed;
pain in the lumbar spine;
abdominal pain;
vaginal bleeding or a brown watery discharge;
discomfort when going to the toilet.
In the case of a fallopian tube pregnancy, there is a risk of rupture in the fallopian tube, and the symptoms that may appear are more violent:
intense, sudden pain in the pelvic or abdominal area;
pain in the shoulder - in case of heavy bleeding, the abdominal and pelvic cavities are flooded with blood;
peritonitis (swelling of the abdominal area);
arterial hypotension;
dizziness and even loss of consciousness, due to the loss of a large amount of blood.
Any of the manifestations that could indicate the rupture of an ectopic pregnancy requires emergency medical assistance, as they can endanger the patient's life.
How does ectopic pregnancy occur?
To understand how ectopic pregnancy occurs, it is first essential to know that the connection between the ovaries and the uterus is made through the fallopian tubes. When the fertilized egg needs to reach the uterus, it will pass through the fallopian tubes.
In the case of ectopic pregnancy, the embryo formed after fertilization of the egg usually gets blocked when passing through the fallopian tubes and no longer reaches the uterus for implantation. It will implant outside the uterus or in a scarred and unusual part of it, and a baby will not develop.
Instead, unusual symptoms will appear in the first trimester and health problems will develop if the pregnancy continues. If you want to compare the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy with those of a normal one, I explained HERE more about how the pregnancy usually develops by weeks in each trimester.
At how many weeks is ectopic pregnancy detected?
Ectopic pregnancy is usually discovered early in pregnancy. Doctors usually diagnose ectopic pregnancies in the first trimester (up to 12 weeks of pregnancy). However, most people discover they have an ectopic pregnancy around eight weeks into their pregnancy.
The gestational age at which an ectopic pregnancy is most frequently confirmed is between 6 and 10 weeks. Symptoms usually appear starting in the fourth week, or 6-8 weeks after the last normal period. You can use a pregnancy calculator to approximate what week of pregnancy you are in.
There are also women who do not notice any unusual symptoms at the beginning of pregnancy. In their case, they may not know they have an ectopic pregnancy until the first ultrasound when the doctor makes the diagnosis, or until more serious symptoms begin to appear as the pregnancy progresses without the fetus developing.
As in the case of a normal pregnancy, ectopic pregnancy is detected by pregnancy tests that measure the level of HCG, or by beta HCG analyzes in the laboratory. I told you HERE how and when you realize you are pregnant.
The HCG hormone level has a slower rate of growth in ectopic pregnancy and therefore the first values measured may be lower, which may lead to a false negative result. Laboratory tests, on the other hand, can identify the presence of the HCG hormone even in the case of ectopic pregnancy much earlier. I told you everything about what other tests are done during pregnancy HERE .
Do you get your period during an ectopic pregnancy?
If you get your period or not with an ectopic pregnancy, it's a dilemma for many women and it's normal to be. Especially knowing that if your periods keep coming non-stop, normally you are missing an important clue and it becomes much more difficult to realize that you are pregnant. So let's talk:
Heavy vaginal bleeding is a sign of ectopic pregnancy, but should not be confused with menstruation. Although an ectopic pregnancy can be asymptomatic at first, periods are usually absent even in the case of an ectopic pregnancy. So no, you most likely won't get your period.
But as I said, heavy bleeding can occur during pregnancy that can easily be confused with menstruation. So the signs to look out for are color and texture. Bleeding specific to ectopic pregnancy is watery and lighter, or heavier and darker in color than regular menstrual bleeding.
When should you go to the doctor?
If you experience sudden pain, of increased intensity, associated with vaginal bleeding, go to a medical check-up immediately. At the same time, if you experience a combination of the previously mentioned symptoms, you need to talk to a doctor to determine what situation you are in.

With the delay of the visit, the complications will also appear and the risk of death will increase. It is important to know that an early medical check-up can prevent the occurrence of complications.
Ectopic pregnancy - Causes
There are several possible causes that lead to an ectopic pregnancy. Among them are:
- pre-existing inflammation of the fallopian tube
- congenital malformations of the fallopian tubes
- long-term use of the IUD
- hormonal imbalances
- abnormal development of the fertilized egg
- absence of an ovary
- endometriosis (endometrial-like tissue fragments are present outside the uterus)
- pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) - inflammation of the female reproductive system, usually caused by a sexually transmitted infection (STI)
- previous ectopic pregnancy – the risk of having another ectopic pregnancy is around 10%
- fertility treatment such as IVF - taking medicines to stimulate ovulation (the release of an egg) may increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy
- smoking
- advanced age – the risk is greatest for pregnant women over 35 years of age
Risk factors - Ectopic pregnancy
In addition, in some patients, the probability of an ectopic pregnancy is increased due to certain risk factors. These include existing conditions, medical history, but also bad habits, such as:
history of ectopic pregnancy
previously induced abortion
surgical interventions on the fallopian tubes
pelvic surgery
the presence of the sterile device at the uterine level
smoking
age over 35 years
inflammatory diseases of the pelvis
appendicitis
infections (Chlamydia trachomatis)
sexually transmitted diseases
Ectopic pregnancies are not always conditioned by the presence of risk factors. About half of women with ectopic pregnancy have no risk factors.
Complications of ectopic pregnancy
The reason why it is so important that an ectopic pregnancy is detected, diagnosed and treated in time is that serious complications can occur.
An ectopic pregnancy cannot be carried to term, it does not support the development of the baby and it is impossible for the fetus to survive. What this type of pregnancy does instead is endanger the health and even the life of the mother.
Because it is not a normal pregnancy that implants in the uterus, it can damage the fallopian tubes and cause heavy bleeding or serious infection. Below are the most common complications of ectopic pregnancy.
Internal bleeding
According to statistics, most ectopic pregnancies occur in a fallopian tube – this is the case for over 90% of ectopic pregnancies. Thus, as the pregnancy progresses, its growth can cause the fallopian tube to rupture and automatically cause very serious internal bleeding in the abdomen.
This can happen anytime between weeks 6 and 16, and blood loss is greater the later the rupture occurs. Internal bleeding can even threaten the patient's life. Of course, the more severe the bleeding, the greater the risk of death. Emergency surgery is needed to stop it.
Fallopian tube damage
If it is not detected in time and appropriate measures are not taken, ectopic pregnancy can cause serious health problems due to damage to the fallopian tubes. The main complications that occur are salpingitis (inflammation of the fallopian tubes) or even rupture of the fallopian tubes.
Complications can be manifested by sudden and sharp stomach pain, heavy bleeding, dizziness, fainting, looking pale, and increased pulse. In severe cases, a ruptured tube can even be life-threatening.
Tubal rupture due to ectopic pregnancy requires emergency treatment. It involves the surgical removal of the remains of the pregnancy. Depending on the severity, the ruptured fallopian tube may also be removed, or a repair procedure may be performed.
Diagnosis - Ectopic pregnancy
It is often difficult to diagnose an ectopic pregnancy from symptoms alone, as they can be similar to other conditions. If you have symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy and a positive pregnancy test, you may be referred to an early pregnancy assessment service for further testing.
These tests include:
vaginal ultrasound - for a close-up image of the reproductive system;
blood tests - to measure the pregnancy hormone, the hCG level tends to be lower and rise more slowly over time than in a normal pregnancy;
laparoscopic surgery - for direct examination of the uterus and fallopian tubes.
Can ectopic pregnancy be seen on ultrasound?
If the pregnancy is confirmed, an ultrasound is performed. This is a non-invasive and non-irradiating method that allows the localization of the embryo to be determined. The doctor may also decide to perform a Doppler ultrasound. This increases the chances of detecting an ectopic pregnancy.
Does the pregnancy test detect ectopic pregnancy?
Since ectopic pregnancy is very similar to intrauterine pregnancy at first, the classic pregnancy test will only tell you if you are pregnant or not. The time when the probability of obtaining a conclusive result for the pregnancy test is starting from the first week of delay of menstruation. The urine test commonly used to identify a pregnancy is based on the detection of the level of HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), the hormone produced in the body in the presence of a pregnancy. Keep in mind, however, that pregnancy tests can also indicate false positives or negatives. You can read in our article the reasons why you can get a false positive pregnancy test.
What you need to know is that a pregnancy test will not distinguish a normal pregnancy from an ectopic one, regardless of whether the HCG dosage is done from urine or blood. Usually, such a pregnancy is detected only after the onset of symptoms or even after its termination.
More interesting information about what they are, how they are done, and how pregnancy tests work can be found in our article All about Pregnancy Tests.
Ectopic pregnancy - Treatment
Unfortunately, the fetus (developing embryo) cannot be saved in an ectopic pregnancy. Treatment is usually needed to remove the pregnancy before it becomes too large.
The main treatment options are:
expectant treatment – your condition is carefully monitored to see if treatment is necessary;
medicine – a medicine is used to stop the growth of the pregnancy;
surgery – surgery is used to remove the pregnancy, usually along with the damaged fallopian tube.
Expectant treatment
If you have no or mild symptoms and the pregnancy is very small or cannot be found, you may just need to be closely monitored, as there is a good chance that the pregnancy will resolve on its own.
Called expectant treatment, the process works something like this:
You will have regular blood tests to check if the level of hCG in your blood is falling - you will have them until the hormone is no longer found.
Additional treatment is given if the hormone level does not decrease or increases.
You will usually have some vaginal bleeding.
You may have stomach pain.
You will be told what to do if you develop more severe symptoms.
The main advantage of this kind of monitoring is that you will not experience any side effects of the treatment. A downside is that there is still a small risk that one of your fallopian tubes will come off (rupture) and you may eventually need treatment.
Drug treatment
If an ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed early, but active monitoring is not adequate, drug treatment may be recommended. This works by stopping the pregnancy from growing and is given as a single injection into the buttocks.

You will not need to stay in hospital after treatment, but regular blood tests will be carried out to check that the treatment is working. Sometimes a second dose is needed and surgery may be needed if it doesn't work.
Ectopic pregnancy operation
In most cases, laparoscopic surgery will be performed to remove the pregnancy before it becomes too large.
During a laparoscopy:
you are given general anesthesia, so you sleep while it is performed;
small cuts (incisions) are made in the abdomen;
a thin viewing tube (laparoscope) and small surgical instruments are inserted through the incisions;
the entire fallopian tube containing the pregnancy is removed if the other tube appears healthy – otherwise, removal of the pregnancy may be attempted without removing the entire fallopian tube.
Removing the affected fallopian tube is the most effective treatment and does not reduce the chances of getting pregnant again. Most women can leave the hospital a few days after surgery, although it may take 4 to 6 weeks to fully recover.
If your fallopian tubes have already ruptured, you will need emergency surgery. The surgeon will make a larger incision in the abdomen to stop the bleeding and repair the fallopian tubes, if possible.
Psychological counseling
For any woman, recovery from an ectopic pregnancy is not easy, and psycho-emotional health will take time to recover, just like physical health. The loss of a pregnancy brings with it an emotional imbalance, which requires special care, so if you feel the need you can turn to family, friends and, last but not least, a psychotherapist or a psychiatrist who could help you.
Can the ectopic pregnancy be eliminated alone?
In few cases, an ectopic pregnancy can be removed by itself, but then the expectant treatment that I was talking about earlier is applied.
Can you still get pregnant after an ectopic pregnancy?
You may want to try for another baby when you and your partner feel physically and emotionally ready. Is it possible after an ectopic pregnancy?
Your doctor will most likely advise you to wait until you have had at least 2 periods after treatment before trying again to allow you to recover. Most women who have had an ectopic pregnancy will be able to get pregnant again, even if they have had a fallopian tube removed. Occasionally, fertility treatment such as IVF may need to be used.
The chances of having another ectopic pregnancy are higher if you've had one before, but the risk is still small. If you do get pregnant again, it's a good idea to let your doctor know as soon as possible so that early scans can be carried out to check that everything is fine.
Recovery after ectopic pregnancy
As a rule, the woman can resume her normal activities about a week after the laparoscopic surgery to remove the ectopic pregnancy.
During the recovery period it is normal to experience abdominal pain and for this very reason it is recommended to continue taking the painkillers indicated by the doctor. It is also very important to keep in close contact with him so that you communicate any problems you encounter.
Nutrition is again an important factor that contributes to a quick and uncomplicated recovery. Eat light foods such as toast, chicken soup, vegetables and fruits with anti-inflammatory properties. You may also experience vaginal bleeding for 1 to 4 weeks after surgery.
Prevention - Ectopic pregnancy
Although no method of prevention completely eliminates the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy, there are still a number of measures you can take to reduce the likelihood of such a medical problem:
prevention of sexually transmitted diseases, which involves limiting sexual partners, using a condom for every sexual contact that does not lead to conception;
quitting smoking before becoming pregnant;
carrying out periodic checks at the gynecologist, to monitor the health of the reproductive system.
Menstruation after ectopic pregnancy
Menstruation after ectopic pregnancy does not differ much from the usual one. What might surprise you, however, is the vaginal discharge that occurs immediately after pregnancy removal surgery.

And since your health is the most important, choose to use ENROUSH absorbent pads created from 100% GOTS certified organic cotton, without traces of chemicals, perfumes, chlorine or plastic. Hypoallergenic and gynecologist-approved, Enroush's organic cotton pads do not cause irritation or allergies, do not unbalance the pH of the intimate area and give you the security you need.
Discover Enroush pads HERE and take your menstrual care to the next level, for you and your health.
In case of ectopic pregnancy, do you get your period?
As ectopic pregnancy does not initially differ in symptoms from intrauterine pregnancy, your period will stop coming once you become pregnant. You can check if you are pregnant with a pregnancy test.
Sex life after ectopic pregnancy
Depending on your experience, your sex life after ectopic pregnancy may or may not change. Like any important, traumatic event, recovery will depend a lot on the psyche. So, once you feel ready to restart your sex life, take it at your own pace, embracing even the initial rough times that are part of the process. If you have a normal pregnancy, we have prepared another article that we invite you to read to find out everything you need to know about sex during pregnancy .
We do, however, have 2 great tips for a healthy sex life:
limit the number of sexual partners
use a condom - it also protects you against an unwanted pregnancy and against many sexually transmitted diseases
Frequently asked questions
If we haven't answered all your questions yet, maybe we can now.
When is the ectopic pregnancy visible on the ultrasound?
By 12 weeks of pregnancy, the doctor can tell if it is ectopic or not. Most of the time, an ultrasound is done to establish this aspect.
When do you realize you have an ectopic pregnancy?
The symptoms of an intrauterine pregnancy do not differ much from those of an ectopic pregnancy. Our advice is to go to the doctor regularly to identify in time if there is a problem and pay attention to the signals your body sends.
What is the beta hcg value in ectopic pregnancy?
In normal pregnancy, the serum beta-HCG level doubles every 48-72 hours until it reaches the level of 10,000-20,000 mIU/mL. In ectopic pregnancy, the beta-HCG serum level increases less, so the values are lower than in normal pregnancy.
A single value is not diagnostic for ectopic pregnancy. Careful analysis by a doctor is needed.
How long does an ectopic pregnancy last?
Usually, in the first months of pregnancy, a doctor identifies whether it is intrauterine or extrauterine. As only the uterus can support and develop a child, an ectopic pregnancy will not survive and will be removed by surgery or drug treatment.
Why is an ectopic pregnancy dangerous?
The ectopic pregnancy, which in over 90% of cases implants in the fallopian tubes, does not allow the development and survival of the fetus. The baby cannot be fed and cannot grow outside the womb. On the other hand, the growth of the pregnancy can lead to serious complications such as rupture of the fallopian tubes and serious internal bleeding, which can even endanger the life of the mother.
Sources used:
NIH, "Risk factors and clinical characteristics associated with a ruptured ectopic pregnancy": https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9276220/
NIH, “Ectopic Pregnancy”: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539860/
Ada, “Ectopic Pregnancy”: https://ada.com/conditions/ectopic-pregnancy/
NHS, “Ectopic Pregnancy”: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/ectopic-pregnancy/
WebMD, “Ectopic Pregnancy: What To Know”: https://www.webmd.com/baby/pregnancy-ectopic-pregnancy
Cleveland Clinic, “Ectopic Pregnancy”: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9687-ectopic-pregnancy
American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology, "Ectopic pregnancy not within the (distal) fallopian tube: etiology, diagnosis, and treatment": https://www.ajog.org/article/S0002-9378(11)02162-4/fulltext
UCDavisHealth, "7 things to know about ectopic pregnancy": https://health.ucdavis.edu/news/headlines/7-things-to-know-about-ectopic-pregnancy/2022/05























