
A mysterious and painful method of contraception? Yes, the IUD may seem difficult to understand, but the more you learn, the more you realize that things are simpler than you thought. In our article you will find out everything you need to know about the IUD, what are its advantages (and disadvantages), how many types of IUDs there are, and what sex is like before and after IUD removal.
What is an IUD?
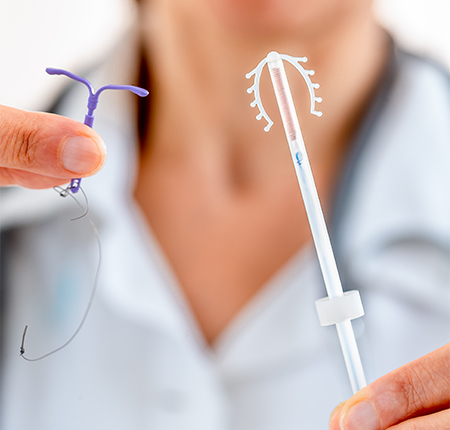
The IUD, or IUD - intrauterine device - is a small device (3-4 cm) usually in the shape of the letter "T" that is inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. In the long run, it is one of the most effective and cheapest reversible contraceptive methods.
The first type of IUD was invented in the early 1900s by a German doctor and was different from what is used now. Today, the IUD can be coated in copper or be based on hormones.

How does an IUD work and what is its effectiveness?
The role of the IUD is to prevent implantation of the egg by thickening cervical secretions. It is important to know that the IUD is a reversible method of contraception, which once removed will not affect your fertility!
It works as a long-term (up to 5, 7 or 12 years) or emergency contraceptive method, ensuring an effectiveness rate of over 95%. Just so you understand, if you use an IUD correctly, your chances of getting pregnant are less than 1%.
What does an sterilette look like?
The IUD is a small T-shaped plastic device about the size of a match, sometimes covered in copper. A plastic string, tied to the end of the IUD, hangs through the cervix into the vagina, but it's very short and you shouldn't feel it - neither you nor your partner.
Types of IUDs
Although IUDs are safe for most women, if you have a copper allergy you should not use a copper device. But let's take them one at a time!
Hormonal contraceptive
The hormonal IUD contains progestin, a hormone found in other contraceptive methods such as pills, vaginal rings or hormonal injections. Its main function is to prevent ovulation and thicken the cervical mucus, while making it difficult for sperm to circulate. 
If fitted on the last day of menstruation, the hormonal intrauterine device starts working immediately. Otherwise, it may take up to 7 days to be effective.
In Romania, IUDs with hormones are most commonly installed and you can buy them in pharmacies.
Copper IUD
The copper intrauterine device has no hormonal effects but works as a "spermicide": copper changes the environment of the uterus, kills sperm and thickens mucus. It can stay in place for up to 10 years and is a highly effective form of contraception.
Regarding the shape of an IUD, various shapes have appeared in recent years: T, U, spherical, cylindrical, ball.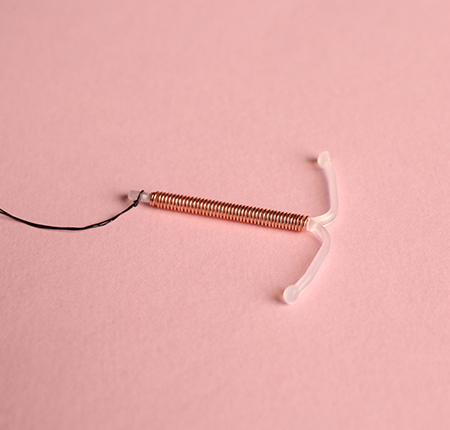 
Analyzes and investigations necessary before moving the IUD
Most healthy women can use an IUD.
But still, what do you need to know before having an IUD fitted? The first step is to talk to your gynecologist and decide together what type of IUD you will have. Then, you will need to do a series of investigations before fitting the IUD.
There are some contraindications, if:
Before the IUD is placed, you will need a gynecological consultation. First, your gynecologist will do a transvaginal ultrasound to make sure everything is fine with your vagina, cervix, and uterus.
Then, you will need to do a pregnancy test, Babes-Pap test, an analysis to detect sexually transmitted diseases and blood tests to determine the level of hemoglobin.
Because the progestin in hormonal IUDs increases the risk of blood clots and high blood pressure, it is recommended that you talk to your doctor if you have any cardiovascular or other health problems.
Last but not least, before fitting the IUD, ask the gynecologist any questions! Make sure you have all the information, and if all tests are favorable, the IUD can be placed during a consultation.
Information about fitting and discarding the IUD
The copper IUD can be inserted at any time of the menstrual cycle, but preferably in the last days of menstruation, or even after the bleeding has stopped. Then, your cervix is open and the insertion is less painful. For the hormonal IUD, insertion is recommended during the first seven days of the menstrual cycle.
How is the IUD fitted?
To get an idea of what happens during the procedure, the gynecologist will insert the chosen IUD after all the tests and the transvaginal ultrasound have been performed. They disinfect your cervix and insert the IUD through the cervical canal. The device will have two wires that will be shortened, 2-3 cm from the cervix, to be able to check its presence later.
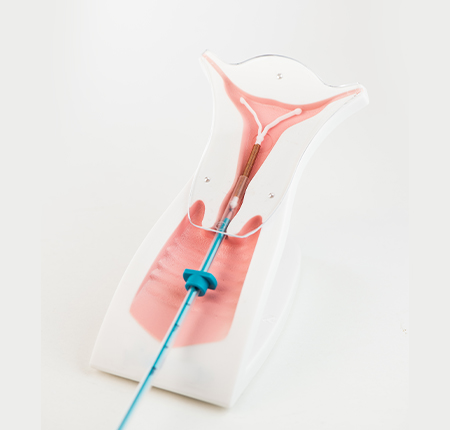
This whole procedure takes around 10 minutes and can be a little uncomfortable. Although fitting an IUD does not require anesthesia, you can request a light local anesthesia and after insertion, you may experience pelvic pain for a few days.
As for giving up the IUD and its extraction, it can be done whenever you want, with the help of the gynecologist. The removal of the IUD is a simple, uncomplicated procedure: with the help of a speculum and forceps, the doctor grasps the wires of the IUD and gently extracts it. You may experience cramping during the procedure, but this is relieved with a pain reliever. Sure, threading sounds simple enough, but don't confuse the procedure with removing a tampon! The only person who can remove the IUD is your doctor.
What can you expect?
During insertion of an IUD, you can expect to feel muscle cramps, dizziness or a feeling of fainting.
You can also expect some side effects, such as headaches, breast tenderness, irregular bleeding (but which settles after the first 6 months), mood swings and menstrual cramps or pain, as the IUD can cause side effects. Most of the time these are mild reactions and resolve on their own.
Side effects of the hormonal IUD may include:
Irregular or no periods, headache, bloating, nausea, sensitivity, low libido.
And the copper IUD can have side effects such as:
Menstrual cramps, back pain, longer, irregular and heavy periods.
In terms of sex, the first contact after the IUD should not be any different from regular sex. Remember: the IUD is inserted into the uterus, not the vagina, so your partner shouldn't feel anything.
Bleeding after IUD insertion - what to expect
After inserting the IUD, we can talk about two types of bleeding: periodic bleeding (ie menstruation), and intermenstrual bleeding. Depending on how heavy they are, use organic menstrual products made from 100% organic cotton and hypoallergenic, and choose an appropriate degree of absorbency.
From the first menstrual bleeding after fitting you can expect it to be heavier than usual. It's normal. But if you notice that it is very abundant or that it does not stop, don't think twice: talk to your doctor.
In the case of intermenstrual bleeding, you can expect vaginal discharge in the form of brown spots or even quite heavy bleeding. How long it normally takes depends on the type of IUD:
Hormonal IUD: You may have daily bleeding for up to 3-6 months after insertion.
Copper IUD: Bleeding can last up to 2-3 months.
After this settling-in period, in most cases only light brown discharge or light bleeding will remain, and these will eventually disappear.

The first sexual intercourse after inserting the IUD
The recommendation of doctors is generally to wait at least 24 hours after insertion before the first sexual contact, because the risk of infection is higher. Also for 24 hours you should avoid hot baths and insert absolutely nothing into the vagina, not even a tampon.
Theoretically, after 24 hours you can have sex with the IUD at any time. Except, of course, the situation where you recently gave birth and the doctor inserted the IUD shortly after postpartum. Your uterus and vagina are still recovering, and in this case you need to wait for the doctor's approval.
Neither you nor your partner should feel the IUD or any discomfort directly caused by it. But because of the side effects that may occur after insertion, sex with the IUD in the first few months may not be as pleasant. Unusual bleeding and abdominal cramps can decrease your libido and lubrication, making your first experiences of IUD sex less comfortable.
What can happen if I can no longer feel the wires from the IUD?
The wires may have moved if you can no longer feel them. This does not mean that the IUD is no longer attached or that it is no longer an effective method of contraception, because most likely everything is still working as it should. However, it is best to pay a visit to the gynecologist's office, so that the doctor can examine you and confirm that everything is fine.
What does it mean if your period is late after inserting the IUD?
During the first 2-3 months after inserting any type of IUD, periods are no longer predictable. Just as they can become more abundant or longer, they can also be delayed. It doesn't mean you're pregnant, just that you're in the adjustment stage. Talk to your doctor if your period is more than 6 weeks late.
It's a more common symptom than you think, and statistics show that 2 out of 10 women who use certain types of hormonal IUDs lose their periods completely after 6-12 months.
Can I have a positive pregnancy test even if I have an IUD?
Intrauterine devices are one of the most effective methods of contraception (>99%). There are indeed very rare cases when a pregnancy can be formed even with an IUD. But the probability of getting pregnant is less than 1%. If you still get a positive pregnancy test, schedule a visit to your gynecologist as soon as possible to see what to do next.
Reactions after removing the IUD
You may decide to remove the IUD either because you want to get pregnant or because your body is rejecting the IUD. It should also be removed if it has expired, if you have become pregnant or if you have contacted a sexually transmitted infection.
Regardless of the reason, reactions you can expect from your body after the device is removed include abdominal cramps and spotting for a few days. If the pain is severe and accompanied by heavy bleeding, fever, chills or foul-smelling discharge, see a doctor.
First period after removing the IUD
The first menstrual bleeding after removing the IUD may be lighter, the same, or heavier. Every body is unique and responds differently. There is a possibility that your period will come normally from the first month. But it may still take a few months for your periods to settle and return to normal.
Is bleeding after removing the IUD normal?
Yes, it is normal to bleed a little after removing an intrauterine device. As long as it's only spotting or light bleeding and no other symptoms (severe pain, fever, unusual discharge) are involved, there's nothing to worry about.
Very heavy bleeding and clot formation are not normal and require medical consultation as soon as possible.
The advantages of an IUD
One of the great advantages of the IUD (whether hormonal or copper) is that it can be used as emergency contraception in the first 120 hours (up to 5 days) after unprotected intercourse, with greater than 90% effectiveness . It is the most effective way to prevent pregnancy after sex, especially if you plan to have a long-term contraceptive method.
The hormonal IUD also has benefits other than contraception, and can be recommended for women with:
Heavy menstruation
Painful periods
Endometriosis
Adenomyosis
Anemia
Uterine fibroids
In addition, the advantages of the IUD include:
Low costs and long-term effectiveness
Ease of use
Decrease in the volume of menstrual bleeding
Decreased cramps
Prevention of endometrial cancer
It does not cause weight gain
Disadvantages of an IUD
At the same time, you must know that both the hormone-based IUD and the copper IUD have their disadvantages, and to give you an idea, we will take them one by one.
Disadvantages of the hormone-based IUD:
Your periods may become heavier and/or more painful (in the first 3-6 months after fitting)
Bleeding may occur between periods
It causes an increased sensitivity of the breasts
It can cause headaches or nausea, mood swings, acne, weight gain
It increases the risk of certain liver diseases and the risk of thrombophilia
It increases the risk of developing ovarian cysts
It leads to hormonal imbalances
As for the copper IUD , it:
Not recommended if you have a copper allergy
May intensify menstrual pain and cause heavier periods, bleeding between periods - in the first 2-3 months
It can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or Wilson's disease
in rare cases, the copper IUD may partially or completely fall out of the uterus and perforate the uterine wall
Rejection symptoms
What happens when the body rejects an IUD? In case of rejection, the IUD will descend from the uterus to the level of the cervix or will be expelled through the menstrual blood. Generally, rejection can happen in the first year of use - especially in the first month - but is very rare.
The risk of expulsion occurs when the IUD was inserted immediately after birth or if you have not had any pregnancy. Symptoms of expulsion are strong uterine contractions and heavy bleeding.
Symptoms of IUD infection
After fitting the IUD, it is recommended to avoid vaginal sex, the use of tampons and baths for 1-2 days, precisely because the risk of infection of the IUD is increased immediately after installation. Among the most common symptoms of infection are:
Heavy bleeding
Unusual or foul-smelling vaginal discharge
Pelvic pains
Pain during intercourse
Fever
Flu-like symptoms (chills, headache, fatigue)
Risks and complications
Like any medical device, the IUD is not without risks and complications, although these are rare. With the copper IUD, people who use it may experience spotting (bleeding) between periods. Very rarely, the IUD can block or perforate the uterus.
As for complications, they are extremely rare, but you need to be aware of them:
Expulsion of the sterile device
Changes in blood pressure or blood clotting
An ectopic pregnancy (outside the uterus)
Infection
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Damage to the uterus
If you have a history of cardiovascular disease, smoke or are over 35, the risks and complications increase after fitting a hormonal IUD. But any irregularities you notice, it is important to contact your doctor at any time after inserting the IUD, especially if symptoms such as:
Chills and fever over 38°C
Unbearable cramps, sharp pain in the stomach
Heavy bleeding
A missed period (on the copper IUD)
A positive pregnancy test
Sex after removing the IUD
After the removal of the intrauterine device, you can theoretically get pregnant immediately because your fertility returns to normal. So if you don't want a pregnancy, use a condom or another method of contraception from the first sexual intercourse without an IUD.
The good news is that unlike insertion, there is no time frame you have to wait to resume your sex life after IUD removal. You can have sex anytime before and after the IUD is removed.
How much does a sterile device cost? (Estimated prices)
The IUD is currently considered the cheapest method of contraception. A copper intrauterine device will cost you around 40-50 lei, and the hormonal one around 500-600 lei, excluding the cost of consultation and insertion by the doctor. But take into account that it provides protection between 5-10 years, and you will not spend on other contraceptive methods.






















