"Itching in the private area when urinating? You have a cold!” is the verdict you've probably heard many times from friends or family. But the sting is not always the same, and the burning and that false sensation that you need to use the toilet - associated with urinary infections - are only a chapter in this large topic.
Stinging can also come from a genital infection, irritation, sexually transmitted diseases or even injuries inside the vagina. The causes of all these things are much more varied than a common cold. So today we get rid of another myth, that vaginal itching automatically means cystitis. Find out what causes them, what symptoms they have, how we treat and how to prevent these stings in the intimate area.
What is vaginal itching?
Stinging in the intimate area, in women, is actually a feeling of discomfort that is manifested by burning, tingling, itching, pain or vaginal stinging. They can have several causes, which we will talk about immediately, but mainly they appear as a result of an imbalance of the vaginal flora, when the tissues in the genital area become inflamed.
These symptoms intensify during sexual intercourse, after it, or when you want to use the toilet. There is also the possibility that their intensity is constant throughout the day, which prevents you from concentrating and carrying out your activities normally.
Causes of stinging in the intimate area
There are many causes that can determine the appearance of stinging, and about those of a medical nature - that is, imbalances of the vaginal flora, bacterial or fungal infections, sexually transmitted diseases - we will tell you in more detail right away.
But before that, we want to tell you about another cause that is easy to overlook, but which often causes many of your discomforts in the genital area, acting on your vagina indirectly: hygiene products used in the intimate area .
The best example? The absorbents that you use month after month and that can irritate your skin every day during menstruation. If you use conventional pads, it's good to know that many of them contain dioxin, chlorine, bleach, plastic, and other chemicals that are toxic to your vulva (even if they're not on the label! ‒ because the manufacturers aren't required to). They can cause you those allergies, itching and irritations that intensify during menstruation. So no, menstruation is not to blame for this discomfort, but menstrual products!
So we recommend you to use only organic absorbents made of 100% organic cotton, made with nothing but natural fibers. Choose the right absorbency level according to your menstrual flow and you will enjoy not only allergy-free periods, but also softer and smoother products for your skin. In addition, Enroush organic cotton pads are dermatologically and gynecologically approved, hypoallergenic and pH neutral, safe for your body.
Bacterial infections
So let's get back to the medical causes that can cause stinging and prickling in your genital area. And we start with bacterial infections ‒ such as bacterial vaginosis ‒ , one of the most common causes of vulvovaginitis and discomfort in the intimate area.
When the balance of your vaginal flora is disrupted, there is an excess of bacteria in the vagina that outnumber the lactobacilli (good bacteria), and this is what the beginning of a bacterial infection looks like. Although it can sometimes be asymptomatic, it is generally manifested by discharge and unusual smell especially after sexual intercourse, pain and stinging of the vagina.
Sexually transmitted diseases
Another cause for any type of discomfort in the intimate area can be a sexually transmitted disease. Infections transmitted by intimate contact can also cause you stings, but also a lot of other unpleasant symptoms such as itching, pain, unpleasant odor, bleeding outside of menstruation and vaginal discharge of abnormal color.
So if you had unprotected sex or with a new partner and then the stinging started, it may be a sign of a sexually transmitted disease:
Trichomoniasis
A very common sexually transmitted disease, trichomoniasis is a urogenital infection that affects women and men equally, even though it is asymptomatic in almost 70% of cases. It is caused by a parasite transmitted from one person to another through sexual contact.
In the case of women, the burning sensation in the intimate area is one of the signs of infection. But it can also be accompanied by other forms of discomfort: itching, redness and stinging in the intimate area, pain during sexual intercourse or urination, unpleasant odor and yellow or green vaginal discharge.
gonorrhea
Another condition that you can contact through unprotected sexual contact from another infected person is gonorrhea, namely infection with a bacterium called "Neisseria gonorrhoeae".
As this bacteria infects the cervix, fallopian tubes, and uterus, symptoms such as bleeding outside of your period, unusual vaginal discharge or inflammation, and vaginal discomfort when you urinate can also occur as a strong burning sensation.
Chlamydia (Chlamydiosis)
Chlamydia can similarly affect you, if you sexually contact the "Chlamydia trachomatis" bacteria from an infected person. Like trichomoniasis, it is a sexually transmitted disease that can often go unnoticed because symptoms appear in only approx. 30% of cases.
But when it manifests itself in symptoms, it can cause stinging and prickling in your genital area, vaginal pain during intercourse or urination, bleeding outside of your period, and heavy vaginal discharge.
Genital herpes
Also in the chapter of diseases that you can contact sexually, we are also talking about genital herpes, another frequent cause of pain in the intimate area or stinging during sexual contact and especially when urinating. Genital herpes can also give you vaginal itching, stinging or burning, inflamed and swollen glands, blisters, changes in vaginal discharge, and other flu-like symptoms.
Although you can treat the symptoms of herpes, unfortunately it is never completely cured, because the virus remains in the body. That is why it is best to avoid infection. Genital herpes is transmitted by skin-to-skin contact with a person who has the virus, and may remain asymptomatic until it becomes active.
Vaginal PH imbalance
Remember what I told you above about the balance between lactobacilli and other bacteria in your vagina? It's a very delicate balance, and sometimes it doesn't take a bacterial infection to upset it. It is enough for the vaginal pH to change and allow the excessive accumulation of other bacteria, and the entire flora of the intimate area will suffer. This will increase your susceptibility to other infections, irritations and inflammations that can cause stinging and burning in your intimate area.
Normally, a healthy vaginal pH is slightly acidic, with a value between 3.8 and 5. If you practice vaginal douching or use shower gels, soaps, detergents or other perfumed products, they can change your pH and its effectiveness in protect your vaginal health. Including your menstrual cycle, unprotected sex, and antibiotic treatments can temporarily alter your vaginal pH and lead to burning in the labia and insides.
Candidiasis
We've talked about bacterial infections, we've talked about sexually transmitted infections, and now we're talking about one last type of infection in this article that can cause itching in a woman's intimate area: yeast infection. Candidiasis is the most common example of infection with a type of fungus called Candida, most often Candida albicans.
We also find Candida normally inside the body and on the skin, including the vagina, without it being dangerous. But when there are imbalances in the vaginal pH and microbiome (for example due to antibiotic treatment, a weakened immune system or hormonal imbalances), this fungus multiplies excessively and causes the infection called candidiasis. Genital itching and burning, unusual vaginal discharge and vaginal pain when urinating or during sexual intercourse can therefore also be caused by such an infection.
Menopause
Menopause is not a direct cause of stinging and pain in the vagina, but it can indirectly cause them. As estrogen levels decline further before and during menopause, vaginal tissue thins, loses lubrication and elasticity, and becomes drier.
This very vaginal dryness can be the reason why you experience vaginal stinging, and the stinging and pain during sex are even more intense without proper lubrication. Especially if you also suffer from hot flashes and night sweats, irritability and fatigue, lack of sexual appetite and insomnia, it is very possible that menopause is the cause of all these forms of discomfort.
Symptoms of stinging in the intimate area
By the term stinging in the intimate area, we mean more than vaginal discomfort. Any type of external or internal genital burning or stinging caused by irritation and inflammation falls into this category. So the symptoms of the sting can manifest themselves:
- at the level of the vagina, but also at the level of the labia and the clitoris
- with an average but constant intensity, or with a low intensity that increases significantly when urinating or during sex
- along with other symptoms (unusual vaginal odor and discharge, non-menstrual bleeding, pain, stinging, itching, redness, swelling, etc.).
Risk factors for vaginal itching
Women prone to vaginal stinging and irritation in the intimate area are actually prone to all the conditions that can manifest with this symptom. So people vulnerable to bacterial infections such as vaginitis, sexually transmitted diseases, fungal infections and vaginal pH disturbances are included in the risk categories.
So the risk factors for the occurrence of vaginal stinging coincide with those of all these conditions, and the people with the greatest predisposition are women who:
- are pregnant
- I use contraceptives
- they underwent antibiotic treatment
- are dealing with diabetes
- have low immunity
- do not protect yourself with a condom during sexual intercourse
- they use conventional absorbents and tampons
- I use scented intimate hygiene products
- they wear tight clothing made of synthetic fibers that do not allow the skin to breathe
- I am menopausal or perimenopausal
When you need to see a doctor
Any untreated infection can lead to complications and more serious health problems. And because basically the medical causes of vaginal stinging are infections ‒ of any type ‒ it is very important to go to the doctor for treatment from the first signs. So as soon as the discomfort appears, we recommend that you visit the gynecologist as soon as possible, especially if:
- you are pregnant (untreated infections can even cause premature birth or miscarriage)
- symptoms intensify
- discomfort is accompanied by pain, itching, inflammation and fever
- you have never had such discomfort before
- you don't know why you are experiencing vaginal itching
- treatment does not make you feel better
- symptoms recur or repeat more than 2 times in the same year
- you have had sexual contact with a person diagnosed with a sexually transmitted disease
Itching in the intimate area: Diagnosis
We advise you not to try to diagnose yourself. The symptoms of various STDs can be very similar, or you may have an STD that doesn't even have any symptoms. So it is almost impossible to make a correct diagnosis on your own, in the absence of tests.
The gynecologist is the only specialist who can correctly diagnose you, according to the information in your medical history, clinical examination and specific analyses. Once the cause of vaginal stinging is correctly diagnosed, the right treatment for that condition can be chosen, after which the stinging in the intimate area will also improve.

Treatments for itching in the intimate area
There are situations when the burning and stinging sensation is neither serious nor dangerous, and it can go away on its own. For example in the following scenario: you took a bubble bath or used scented toilet paper/absorbents, they caused irritation, but you quickly noticed the discomfort and stopped using the same products. In the absence of agents that aggravate your allergy, the sting may go away even without treatment.
Likewise, it's normal to feel vaginal pain and slight stinging, tingling, or prickling in the genital area during pregnancy as new changes occur in the blood vessels, nerves, and vaginal tissue. And these can improve on their own, without any specific treatment.
But not all situations are so simple, and in cases where a genital infection is the cause of the sting, the symptoms can worsen without proper treatment.
That's why we recommend using hypoallergenic organic cotton daily absorbent pads . This way you can notice any abnormal discharge in time and confirm that the stinging is not caused by an allergy to toxic chemicals, an infection, a hormonal imbalance or another health problem.
Regardless of the diagnosis, all of these conditions will need treatment. That is why we recommend that you go to the gynecologist as soon as possible, who can recommend:
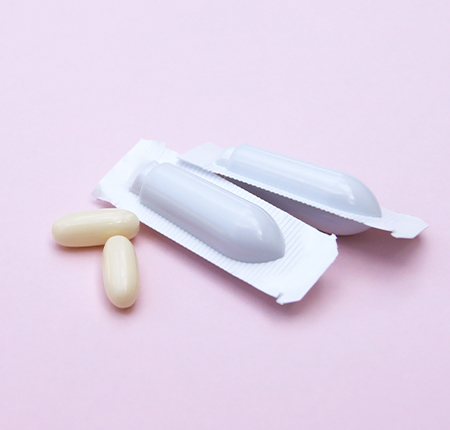
- Eggs for stinging in the genital area : for example in the case of Candida infections, eggs for stinging containing antifungal drugs can be prescribed
- Antibiotics : is the specific treatment of sexually transmitted diseases such as Chlamydia
- Ointments and creams for stinging in the intimate area : for itching and discomfort caused, for example, by genital herpes, the specialist doctor may recommend the application of an ointment that will heal the lesions created by this virus
- Lubricants : for women who suffer from vaginal dryness, for example at menopause, the doctor may recommend the use of lubricants before intercourse, to reduce the discomfort
- Hormonal treatments : when the hormonal imbalance is the one causing the intimate discomfort
Possible complications regarding vaginal stinging
As we told you above, if you do not treat vaginal itching, it means that you are not actually treating the condition that causes it either, and this can lead to complications such as:
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Infertility
- scar
- Transmission of the disease to the fetus: if the mother suffers from a sexually transmitted disease that she does not treat
- Premature birth or pregnancy loss: especially if the mother is infected with Chlamydia, trichomoniasis or genital herpes
- HIV infection: people with untreated STDs are more likely to get HIV if they have sex with another infected person
Natural remedies for stinging in the intimate area
Before you try various teas for itching in the genital area or other natural treatments, keep in mind that home remedies do NOT replace a visit to the gynecologist, nor do they help you diagnose yourself. Without knowing the cause of the problem, you cannot treat it, and that is why we advise you not to use any kind of treatment without the doctor's approval.
Only after a specialist consultation and discussions with a gynecologist, if he confirms that it's okay, here are some things you could try at home to relieve your vaginal itching:
- Cold compresses : they can give you immediate relief from vaginal stinging, and even itching. (Caution, itching can have other causes than stings. If you face this sensation, maybe the article in which we focused exclusively on the causes of vaginal itching and what you can do to get rid of them will help you).
- Salt water baths : Because salt has the potential to slow the spread of bacteria, a warm bath with half a teaspoon of salt may help reduce symptoms of inflammation.
- Cotton underwear : Cotton's natural fibers let your skin breathe and don't trap sweat, leaving your skin dry. Without a moist environment conducive to the multiplication of fungi, your intimate area is protected from fungal infections and the discomfort they cause.
- Consumption of probiotics : studies suggest that probiotics contribute to maintaining an optimal level of lactobacilli in the vagina, playing an essential role in the balance of the vaginal flora and relieving discomfort. So you can consume foods rich in probiotics such as yogurt or honey.
- Chamomile tea : it is recommended especially if you suffer from candidiasis, because it has bactericidal and anti-inflammatory properties that can calm the stinging sensations.
- Baking soda : Another natural remedy for candidiasis, baking soda baths for 20-25 minutes can help reduce discomfort due to baking soda's antifungal properties.
Methods of preventing vaginal stinging
Although the causes of stinging in the intimate area are multiple and varied, the prevention methods are neither complicated nor too numerous. The most important thing is to follow the basic rules for proper hygiene. So to prevent such symptoms:
- Protect yourself : use a condom with every sexual contact and especially if you have a new partner.
- Avoid products that can cause irritation : no perfumes, parabens and artificial ingredients in the intimate area, whether we're talking about detergents, shower gels, soaps, menstrual products, bubble baths or toilet paper.
- Use a natural intimate gel : if you still prefer to use intimate hygiene products, choose only natural ingredients that are safe for your vulva. Enroush intimate gel is formulated together with specialist doctors in dermatology and gynecology, with 95% natural ingredients that have antibacterial properties and 87% effectiveness against Candida albicans.
- Choose organic cotton : for underwear, clothes but also for menstrual products, because it lets your skin breathe much better than synthetic fibers.
- Go to gynecological consultations regularly : many urogenital infections are asymptomatic, and routine check-ups can help you detect and treat them in time, to prevent discomfort, stinging and possible complications.