
The health of your uterus and genitals is very important for a functioning reproductive system. Untreated, inflammation of the uterus and ovaries can lead to infertility or other complications. Therefore, do not ignore pelvic pain or abnormal vaginal discharge. They can be signs of an infection, telling you that you need to see a doctor. Today we are talking about adnexitis, or pelvic inflammatory disease, which we often mistakenly call the "ovarian cold".
What is adnexitis (pelvic inflammatory disease)?
Adnexitis, which we also call pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), is a gynecological infection of the internal female genital organs. It can affect the uterus, fallopian tubes, cervix and ovaries, generally in young, sexually active women. If left untreated, BIP can lead to infertility.
Because it is a pelvic inflammation, which affects the female reproductive organs, adnexitis is often referred to in popular terms as "ovarian cold". But the term is wrong. BIP is no ordinary cold. It has neither the causes nor the symptoms of a cold, and its consequences can be serious for female reproductive function.
Adnexitis or cystitis (ovarian cold) - What's the difference?
The symptoms and their location in the pelvic area of the woman explain why people confuse cystitis with adnexitis. But there are a lot of differences between the two, from causes and treatment to long-term consequences.
Cystitis is actually the "ovarian cold", a bacterial infection in the urinary system (bladder, urethra, ureter and kidneys) that causes inflammation of the bladder. Cystitis, which we talked more about HERE , can appear as a result of bacteria entering the urinary tract, and sometimes as a negative effect of certain medications or poor hygiene.

Adnexitis, on the other hand, occurs when bacteria enter the vagina, not the urinary tract, and affect the reproductive system—again, not the urinary system. We cannot call it "ovarian cold", because the ovaries are only infected if the adnexitis is untreated and reaches an advanced stage. Otherwise, problems occur in the cervix or uterus, infecting the fallopian tubes.
Types of annexation
Depending on how advanced the infection is, pelvic inflammatory disease is divided into two categories: acute and chronic. The symptoms of the two are not very different, but it is chronic adnexitis that can lead to infertility.
Acute adnexitis
Acute adnexitis is the first stage of infection, which can also be a cause of cervicitis and endometritis. Among the characteristic symptoms we find:
Sudden and intense pelvic pain, between the lower abdomen and lumbar region;
Sensation of tension in the abdominal muscles;
Irregularities of the menstrual cycle.
Because we are talking about an inflammatory disease, the fallopian tubes can also increase in volume or fill the lumen with purulent secretions, because of which the infection can spread to the peritoneum and ovaries.
Chronic adnexitis
In the absence of treatment of acute adnexitis, the disease reaches the chronic stage, which is characterized by the possibility that the fallopian tubes swell or deform, but also by other symptoms:
Vaginal discharge, spotting between periods;
Subfebrile body temperatures;
Loss of appetite;
Migraines.
The fact that chronic adnexitis ends up inflaming both the uterus and the ovaries and the peritoneum is actually the reason why it can cause infertility.
Annexitis - Symptoms:
Unfortunately, it is difficult to realize that we have adnexitis because the symptoms are varied, mild and sometimes non-existent, which makes them easy to overlook. 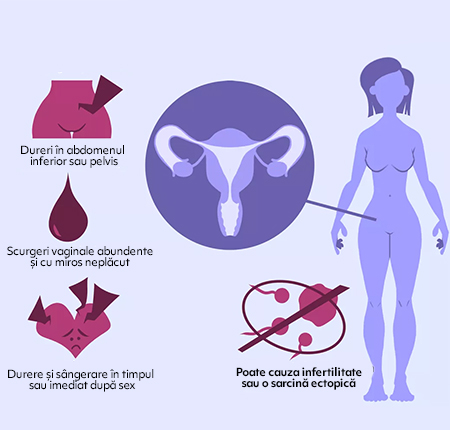
But in general, BIP begins with a feeling of discomfort in the lower abdomen, which sometimes feels more intense on one side and extends to the inner thigh area. This is only the first phase, after which among the most common symptoms of annexitis we find, on a physical level:
Vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor;
Different consistency or yellow-green color of vaginal secretions;
Subfebrile states or fever up to 39°C;
Abdominal cramps and acute pain;
Frequent need to go to the toilet;
The sensation of pain or stinging when urinating;
Discomfort or pain during sexual intercourse;
Bleeding or pain after intercourse;
Heavy flow and intense pain during menstruation;
Bleeding between periods.
In the advanced stages of annexitis, it can also be manifested by:
Vomiting conditions;
Dizziness or fainting;
Chills, tremors or profuse sweating.
In order to better manage all the unpleasant symptoms you are going through, you must go to the doctor as quickly as possible for appropriate treatment.
But it is equally important to pay close attention to personal hygiene. The more natural and healthy care you give yourself, the more you prevent inflammation and pain from worsening. We are by your side with everything you need for menstrual care and every day of the month, with organic and natural products that do not cause irritation or allergies.

Keep in mind that with pelvic inflammatory disease the symptoms are not only physical, but also behavioral and mental. So, other changes you may notice when you have BIP include:
Mood swings;
Constant and excessive irritability;
Feeling of repulsion towards the partner;
Reduction of sexual appetite.
Adnexitis - Causes pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
As we said above, adnexitis occurs when bacteria from the vagina or cervix infects the fallopian tubes and uterus. There are many and varied bacteria that can do this, but the best known are sexually transmitted infections, which lead to the multiplication of bacteria such as strep and staphylococci, which travel up the fallopian tubes through the female genitalia.
However, there are other causes of annexation. For example, although it rarely happens, it is possible for the disease to spread through infected abdominal organs, for example in appendicitis. So let's point out as many of the causes of annexation as possible:
Infections with Gonorrhea, Chlamydia or Mycoplasma: are the most common causes of adnexitis and are transmitted during unprotected sexual contact;
Infections occurring during menstruation, after a birth or after an abortion: they happen rarely and are caused by bacteria that enter the reproductive system, with the modification of the normal protective barrier of the cervix;
Bacteria entered the reproductive system during a procedure that requires the insertion of certain instruments into the uterus, which happens very rarely;
Imbalance of the vaginal flora, due to too frequent vaginal washes;
Surgery on the genitals;
Neck wound;
Bacterial vaginitis;
Appendicitis.
BIP risk factors
Although we have no official statistical data on the predisposition of women to adnexitis, there are an estimated one million women a year who have an episode of adnexitis. It has been observed that pelvic inflammatory disease occurs most often in sexually active young women, and menopausal or postmenopausal adnexitis is rarely diagnosed.
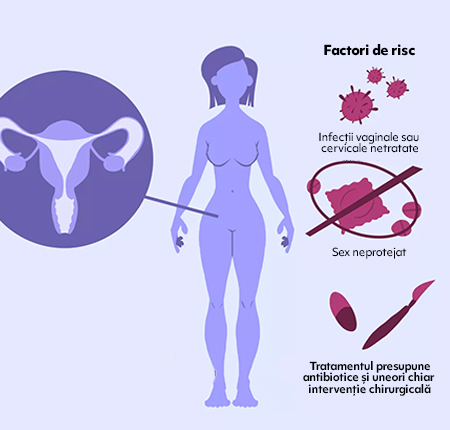
Patients around 25 years of age, who have several sexual partners and do not use protective contraceptive methods such as condoms, are mainly prone. With these things in mind, you may be at higher risk of BIP if:
You are around 25 years old;
You are sexually active with several partners or with a new one;
You have sexual contact with someone else who has multiple partners;
You have sex without a barrier method of contraception like a condom;
You do vaginal washes without the doctor's recommendation;
You have had BIP or other sexually transmitted diseases in the past;
You have recently had an intrauterine device (IUD) inserted - very low risk in the first 3 weeks;
Your immune system is weakened.
When should you go to the doctor?
It would be advisable to go to the doctor as soon as you notice any symptoms that make you suspect that you have adnexitis, be it pelvic pain, unusual vaginal discharge or low-grade fever.
Virtually any vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor, pain during sexual contact, bleeding between periods or discomfort during urination can indicate the presence of a sexually transmitted disease. And correct and early treatment can prevent the development of pelvic inflammatory disease.
So it is important first of all to mention to the doctor any change in the menstrual cycle, vaginal secretions or any other symptom related to intimate health; and secondly, for the gynecologist to make the final diagnosis.
Also, if you have severe pain in the lower abdomen, nausea and vomiting, dizziness and fainting, fever over 38.3℃ with chills, tremors, profuse sweating or abnormal vaginal discharge, adnexitis becomes a medical emergency and you must get to the a consultation.
BIP Diagnostic
The diagnosis of pelvic inflammatory disease is not made after a single test, but is based on a series of elements that indicate its presence. Let's see how to make a BIP diagnosis correctly:
- Visit to the gynecologist: as we said above, a correct diagnosis will only be made by the gynecologist;
- Medical history assessment: the doctor may ask you questions about your sex life, contraceptive methods used and history of sexually transmitted diseases;
- Symptom assessment: This is the stage where you tell your doctor all the signs and symptoms you've noticed - even the smallest changes;
- Clinical examination: initially, the doctor performs a palpation to detect and locate the inflammations;
- Vaginal discharge testing: Your doctor may take a sample of your vaginal discharge to test for the presence of certain bacteria.
After initial testing, the diagnosis may still be unclear. In this case, the doctor may recommend further investigations with other tests and analyses:
Blood tests;
Urinalysis;
Pregnancy test;
Pelvic ultrasound;
Colposcopy;
Laparoscopy;
Endometrial biopsy.
Treatment of adnexitis / pelvic inflammatory disease
Once diagnosed, there are specific treatments for adnexitis. However, they depend on the medical history and the severity of the infection. So, depending on the stage of the disease and the needs of each patient, the doctor will choose the most suitable treatment plan for pelvic inflammatory disease.
Throughout the treatment, you can also receive other recommendations aimed at preventing reinfection and ensuring that the treatment works optimally:
Sexual abstinence until complete healing;
Rest and avoidance of physical exertion;
Avoiding low temperatures;
Treatment of the sexual partner, even if they do not have symptoms;
Abandoning the IUD, especially if it was inserted just before the infection;
Regular medical control during treatment to determine if it is effective.
Also, after completing the treatment, it will be recommended to repeat all the investigations. If the adnexitis does not heal completely, other complications may occur. So a new test is necessary for the doctor to make sure that all the bacteria are completely gone.
Antibiotic treatment for adnexitis
Antibiotic treatment for adnexitis is prescribed to fight the bacterial infection and cure if the disease is in an early stage or the symptoms are mild. The doctor may recommend a combination of antibiotics when more than one bacteria is causing the infection. Antibiotics can be in the form of pills, injections or eggs.
The treatment must be followed for the entire period it was prescribed even if the symptoms improve sooner. Depending on the situation, intravenous administration may be necessary - in which case the treatment is carried out in the hospital. For example, for pregnant women who have a severe form of the disease, antibiotics will be administered intravenously.
Egg treatment for pelvic inflammatory disease
We have already established that the doctor can also recommend eggs with antibiotics for adnexitis. But eggs with propolis or other herbal eggs can also be recommended, to relieve pain through their anesthetic effect.
Anti-inflammatory treatment for adnexitis
Along with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs can also be recommended, with the aim of reducing local discomfort, namely pain in the ovaries (the feeling of an inflamed ovary or inflamed ovaries) and in the lower abdomen.
Surgical treatment for BIP
Very rarely, surgical treatment may also be necessary. Some of the situations in which the doctor recommends surgical intervention are:
When the patient's body does not respond to antibiotic treatment: the purpose of the operation is, in this case, the total removal of the infection and fluid sacs from the fallopian tubes or from the uterine mucosa;
When the infection continues to spread: the doctor can remove the fallopian tubes, thus making it impossible for the patient to become pregnant;
If an abscess develops with a large volume or with a risk of rupture: the doctor will perform a drainage.
Does the natural treatment for adnexitis work?
The immune system plays a very important role in the body's ability to fight bacteria and, by implication, pelvic inflammatory disease. With a weakened immune system, also affected by antibiotics, there is a possibility of BIP relapse, with the return of symptoms. To prevent this situation, treatment with natural food supplements to strengthen the immune system can be effective.
So in addition to the medicines recommended by the gynecologist, taking a naturopathic treatment can help speed up healing and prevent recurrence. Among the most used natural therapies in BIP we find those with:
Vitamin C;
Zinc;
Probiotics;
Echinacea;
Black currant buds;
Raspberry shoots.
Complications Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Being an inflammation of the female reproductive organs, BIP is the reason why these organs no longer perform their main function correctly - that of reproduction. This means that the patient cannot become pregnant, and for this reason, the most common complication of adnexitis is infertility.
If the disease is treated early and correctly, the reproductive organs begin to perform their function again, infertility disappears and the patient can become pregnant again. There are rare exceptions, when due to other complications, infertility can remain permanent.
Also, in the absence of proper treatment, other complications of chronic adnexitis can occur:
- Pelvic pain can become chronic and not go away for months or even years;
- Bacteria can spread to neighboring organs, even the liver;
- Rupture of an abscess (peritonitis) in the fallopian tubes or ovaries may occur;
- Adhesions and bags of pus may occur that can create permanent damage to the reproductive organs or spread to other organs in the pelvic area;
- Damage and scarring to the fallopian tubes during BIP can prevent the fertilized egg from reaching the uterus, blocking it in the fallopian tube, which is why BIP is one of the most important causes of ectopic pregnancy;
- BIP can recur if the treatment regimen has not been followed to the end. Also, an organism that has suffered from BIP in the past is prone to be affected again;
- Depression can occur as a result of guilt and lack of fulfillment, feelings that can be felt together with the lack of ability to give life (infertility).
How can annexitis be prevented?
It is not difficult to prevent annexation when you are well informed. Preventive measures for pelvic inflammatory disease are simple and easy to implement. It is important to take care of the health of your intimate area both in terms of hygiene and sexual health:
Use a condom every time you have sexual contact;
Be careful about the sexual partners you choose.
Avoid vaginal douches that increase the risk of infections by unbalancing the vaginal flora;
Get the right information about contraceptive methods: just because they protect you from an unwanted pregnancy does not mean that they also protect you from sexually transmitted diseases or developing adnexitis. Only barrier methods such as condoms can lower the risk of infection;
Get tested as soon as possible if you suspect you have adnexitis or any sexually transmitted disease (ie as soon as you notice unusual vaginal discharge, pelvic pain or other symptoms);
Treat any sexually transmitted disease as soon as possible to prevent the spread of bacteria and the development of pelvic inflammatory disease;
Your partner must also be tested and treated if you have been infected;
Don't put off regular gynecological visits, because medical check-ups at regular intervals are essential to prevent any kind of health problem;
Take care of your intimate and sexual hygiene.
Frequently Asked Questions
We try to be close to you with information as clear as possible and from reliable sources. That is why below we will also address some of the most frequently asked questions about BIP, such as whether adnexitis is transmitted to men or what danger it poses to pregnancy.
But we strongly recommend that you discuss any concerns about adnexitis or your intimate health with your gynecologist. Knowing your medical history and being a specialist doctor, he is in the best position to give you the most appropriate answers and recommendations.
Can men get pelvic inflammatory disease?
Adnexitis affects the female reproductive organs. So pelvic inflammatory disease cannot develop in men, but only in women, because it is, by definition, an infection that develops when bacteria from the vagina ascends to the uterus and fallopian tubes during sexual intercourse.
But even if men can't get this disease, they can still be affected by other sexually transmitted infections. For example, they can be infected with Gonorrhea or Chlamydia and can transmit these bacteria to their partner (respectively Neisseria gonorrhoeae or Chlamydia trachomatis), which can further develop BIP in the woman's body.
Can the annex be transferred to the partner?
Adnexitis occurs especially when a sexually transmitted disease is untreated, a disease that can be transmitted through unprotected sex. So the appendicitis itself is not transmitted to the partner, but the bacteria that caused it could be transmitted. So, even if a man can't BIP, he can pass the infection on to a woman, who can later develop pelvic inflammatory disease.
Is annexation dangerous in pregnancy?
Developed before pregnancy, adnexitis is one of the main causes of ectopic pregnancy. But it is also possible to develop with pregnancy, and symptoms appear in the second trimester.
Specialized studies (PMID: 35405372) tell us that adnexitis in pregnancy is a rare condition, but one that can have serious health consequences. Although it has not been studied enough to give us a clear perspective, pelvic inflammatory disease in pregnancy should be diagnosed and treated as soon as possible to prevent surgical interventions such as laparotomy or removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes (salpingo-oophorectomy).






















